基于k8s部署jenkins
环境准备
可以使用的k8s集群。可以参考kubespray部署k8s集群:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/367564005
创建命名空间
独特的命名空间提供了额外的隔离层,并且可以对连续集成环境进行更多控制。通过在终端上键入以下命令为 Jenkins 部署创建命名空间:
kubectl create namespace jenkins使用以下命令列出现有命名空间,输出确认 jenkins 命名空间已成功创建。
kubectl get nsNAME STATUS AGE
default Active 30h
external-configuration Active 32m
jenkins Active 29h
kube-node-lease Active 30h
kube-public Active 30h
kube-system Active 30h
permission-manager Active 30h使用 Helm v3 安装 Jenkins
典型的 Jenkins 部署由一个控制器节点和一个或多个代理(可选)组成。为了简化Jenkins的部署,我们将使用Helm来部署Jenkins。Helm 是 Kubernetes 的包管理器,它的包封装格式称为chart(制品)。GitHub 上提供了许多社区开发的chart。
Helm Charts 提供应用程序的一键式部署和删除,使那些几乎没有容器或微服务经验的人更容易采用和开发 Kubernetes 应用程序。
环境准备
helm v3版本工具的安装:https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/
git clone https://github.com/helm/helm.gitcd helmmake配置helm
安装并正确设置 Helm 后,按如下方式添加 Jenkins 存储库:
helm repo add jenkinsci https://charts.jenkins.iohelm repo updateJenkins repo 中的 helm charts 可以用以下命令列出:
helm search repo jenkinsci创建持久卷
为什么需要创建持久卷?Jenkins 控制器 pod创建一个持久卷。这将防止我们在重新启动minikube时丢失Jenkins控制器的整个配置和工作。
创建一个名为 jenkins-pv 的卷:
cat jenkins-volume.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: jenkins-pv
namespace: jenkins
spec:
storageClassName: jenkins-pv
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
capacity:
storage: 20Gi
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
hostPath:
path: /data/jenkins-volume/启动它
kubectl apply -f jenkins-volume.yaml创建serviceAccount
在 Kubernetes 中,服务帐户用于为 Pod 提供身份。想要与 API 服务器交互的 Pod 将使用特定的服务帐户进行身份验证。默认情况下,应用程序将以其default运行的命名空间中的服务帐户身份进行身份验证。这意味着,例如,在test命名空间中运行的应用程序将使用命名空间的默认服务帐户test。
我们将创建一个名为 jenkins 的服务帐户:
cat jenkins-sa.yaml---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: jenkins
namespace: jenkins
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate:"true"labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
name: jenkins
rules:
- apiGroups:
-*resources:
- statefulsets
- services
- replicationcontrollers
- replicasets
- podtemplates
- podsecuritypolicies
- pods
- pods/log
- pods/exec
- podpreset
- poddisruptionbudget
- persistentvolumes
- persistentvolumeclaims
-jobs- endpoints
- deployments
- deployments/scale
- daemonsets
- cronjobs
- configmaps
- namespaces
- events
- secrets
verbs:
- create
- get
- watch
- delete
- list
- patch
- update
- apiGroups:
-""resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- update
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate:"true"labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
name: jenkins
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: jenkins
subjects:
- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts:jenkins应用它
kubectl apply -f jenkins-sa.yaml安装jenkins
将部署 Jenkins,包括 Jenkins Kubernetes 插件。详情请参阅官方chart。
也可以根据自己的需求修改相应的配置
把jenkins包拉取到本地执行
helm pull jenkinsci/jenkins
ls
jenkins-3.3.18.tgz
解压
tar xzf jenkins-3.3.18.tgz
cd jenkins
ls
CHANGELOG.md Chart.yaml README.md templates tests Tiltfile VALUES_SUMMARY.md values.yaml参考values.yaml模板修改添加自己的需求。
我这里是另外编写一个名外jenkins-values.yaml 的文件
1、修改相应配置项
- serviceType:
默认是ClusterIP的类型。如果是在VM上实验,建议改成nodePort类型。
serviceType: ClusterIPserviceType: NodePortnodePort: 30080 - storageClass:
先不使用storageClass
persistence:
enabled: false- serviceAccount:
serviceAccount刚刚我们已经手工创建了,所以这里选择false
serviceAccount:
create:falseService account name is autogenerated by defaultname: jenkins
annotations:{}- installPlugins:
我们可以自定义安装一些插件
installPlugins:
- kubernetes:1.29.4
- workflow-aggregator:2.6
- git:4.7.1
- configuration-as-code:1.51插件我们可以先不安装,网速问题可能会一直安装不成功导致pod无法启动
installPlugins:[]- kubernetes:1.29.4- workflow-aggregator:2.6- git:4.7.1- configuration-as-code:1.51我的修改完成后的values文件是这样的。大家也可以自己按照自己的需求去改。
cat ../jenkins-values.yaml
Default values for jenkins.
This is a YAML-formatted file.
Declare name/value pairs to be passed into your templates.
name: value
Overrides for generated resource names
See templates/_helpers.tpl
nameOverride:
fullnameOverride:
namespaceOverride:
For FQDN resolving of the controller service. Change this value to match your existing configuration.
ref: https://github.com/kubernetes/dns/blob/master/docs/specification.md
clusterZone: "cluster.local"
renderHelmLabels: true
controller:
Used for label app.kubernetes.io/component
componentName: "jenkins-controller"
image: "jenkins/jenkins"
tag: "2.277.4-jdk11"
imagePullPolicy: "Always"
imagePullSecretName:
Optionally configure lifetime for controller-container
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command:
- "uname"
- "-a"
disableRememberMe: false
numExecutors: 0
configures the executor mode of the Jenkins node. Possible values are: NORMAL or EXCLUSIVE
executorMode: "NORMAL"
This is ignored if enableRawHtmlMarkupFormatter is true
markupFormatter: plainText
customJenkinsLabels: []
The default configuration uses this secret to configure an admin user
If you dont need that user or use a different security realm then you can disable it
adminSecret: true
hostNetworking: false
When enabling LDAP or another non-Jenkins identity source, the built-in admin account will no longer exist.
If you disable the non-Jenkins identity store and instead use the Jenkins internal one,
you should revert controller.adminUser to your preferred admin user:
adminUser: "admin"
adminPassword:
admin:
existingSecret: ""
userKey: jenkins-admin-user
passwordKey: jenkins-admin-password
This values should not be changed unless you use your custom image of jenkins or any devired from. If you want to use
Cloudbees Jenkins Distribution docker, you should set jenkinsHome: "/var/cloudbees-jenkins-distribution"
jenkinsHome: "/var/jenkins_home"
This values should not be changed unless you use your custom image of jenkins or any devired from. If you want to use
Cloudbees Jenkins Distribution docker, you should set jenkinsRef: "/usr/share/cloudbees-jenkins-distribution/ref"
jenkinsRef: "/usr/share/jenkins/ref"
Path to the jenkins war file which is used by jenkins-plugin-cli.
jenkinsWar: "/usr/share/jenkins/jenkins.war"
Overrides the default arguments passed to the war
overrideArgs:
- --httpPort=8080
resources:
requests:
cpu: "50m"
memory: "256Mi"
limits:
cpu: "1000m"
memory: "2048Mi"
Environment variables that get added to the init container (useful for e.g. http_proxy)
initContainerEnv:
- name: http_proxy
value: "http://192.168.64.1:3128"
containerEnv:
- name: http_proxy
value: "http://192.168.64.1:3128"
Set min/max heap here if needed with:
javaOpts: "-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
jenkinsOpts: ""
If you are using the ingress definitions provided by this chart via the `controller.ingress` block the configured hostname will be the ingress hostname starting with `https://` or `http://` depending on the `tls` configuration.
The Protocol can be overwritten by specifying `controller.jenkinsUrlProtocol`.
jenkinsUrlProtocol: "https"
If you are not using the provided ingress you can specify `controller.jenkinsUrl` to change the url definition.
jenkinsUrl: ""
If you set this prefix and use ingress controller then you might want to set the ingress path below
jenkinsUriPrefix: "/jenkins"
Enable pod security context (must be `true` if podSecurityContextOverride, runAsUser or fsGroup are set)
usePodSecurityContext: true
Note that `runAsUser`, `fsGroup`, and `securityContextCapabilities` are
being deprecated and replaced by `podSecurityContextOverride`.
Set runAsUser to 1000 to let Jenkins run as non-root user jenkins which exists in jenkins/jenkins docker image.
When setting runAsUser to a different value than 0 also set fsGroup to the same value:
runAsUser: 1000
fsGroup: 1000
If you have PodSecurityPolicies that require dropping of capabilities as suggested by CIS K8s benchmark, put them here
securityContextCapabilities: {}
drop:
- NET_RAW
Completely overwrites the contents of the `securityContext`, ignoring the
values provided for the deprecated fields: `runAsUser`, `fsGroup`, and
`securityContextCapabilities`. In the case of mounting an ext4 filesystem,
it might be desirable to use `supplementalGroups` instead of `fsGroup` in
the `securityContext` block: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/67014issuecomment-589915496
podSecurityContextOverride:
runAsUser: 1000
runAsNonRoot: true
supplementalGroups: [1000]
capabilities: {}
servicePort: 8080
targetPort: 8080
For minikube, set this to NodePort, elsewhere use LoadBalancer
Use ClusterIP if your setup includes ingress controller
serviceType: NodePort
nodePort: 30080
Jenkins controller service annotations
serviceAnnotations: {}
Jenkins controller custom labels
statefulSetLabels: {}
foo: bar
bar: foo
Jenkins controller service labels
serviceLabels: {}
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-backend-protocol: https
Put labels on Jenkins controller pod
podLabels: {}
Used to create Ingress record (should used with ServiceType: ClusterIP)
nodePort:
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=4000
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
jmxPort: 4000
Optionally configure other ports to expose in the controller container
extraPorts: []
- name: BuildInfoProxy
port: 9000
List of plugins to be install during Jenkins controller start
installPlugins: []
- kubernetes:1.29.4
- workflow-aggregator:2.6
- git:4.7.1
- configuration-as-code:1.51
Set to false to download the minimum required version of all dependencies.
installLatestPlugins: false
List of plugins to install in addition to those listed in controller.installPlugins
additionalPlugins: []
Enable to initialize the Jenkins controller only once on initial installation.
Without this, whenever the controller gets restarted (Evicted, etc.) it will fetch plugin updates which has the potential to cause breakage.
Note that for this to work, `persistence.enabled` needs to be set to `true`
initializeOnce: false
Enable to always override the installed plugins with the values of controller.installPlugins on upgrade or redeployment.
overwritePlugins: true
Configures if plugins bundled with `controller.image` should be overwritten with the values of controller.installPlugins on upgrade or redeployment.
overwritePluginsFromImage: true
Enable HTML parsing using OWASP Markup Formatter Plugin (antisamy-markup-formatter), useful with ghprb plugin.
The plugin is not installed by default, please update controller.installPlugins.
enableRawHtmlMarkupFormatter: false
Used to approve a list of groovy functions in pipelines used the script-security plugin. Can be viewed under /scriptApproval
scriptApproval: []
- "method groovy.json.JsonSlurperClassic parseText java.lang.String"
- "new groovy.json.JsonSlurperClassic"
List of groovy init scripts to be executed during Jenkins controller start
initScripts: []
- |
print adding global pipeline libraries, register properties, bootstrap jobs...
name is a name of an existing secret in same namespace as jenkins,
keyName is the name of one of the keys inside current secret.
the name and keyName are concatenated with a - in between, so for example:
an existing secret "secret-credentials" and a key inside it named "github-password" should be used in Jcasc as ${secret-credentials-github-password}
name and keyName must be lowercase RFC 1123 label must consist of lower case alphanumeric characters or -,
and must start and end with an alphanumeric character (e.g. my-name, or 123-abc)
additionalExistingSecrets: []
- name: secret-name-1
keyName: username
- name: secret-name-1
keyName: password
additionalSecrets: []
- name: nameOfSecret
value: secretText
Generate SecretClaim resources in order to create Kubernetes secrets from HashiCorp Vault using kube-vault-controller.
name is name of the secret that will be created in Kubernetes. The Jenkins fullname is prepended to this value.
path is the fully qualified path to the secret in Vault
type is an optional Kubernetes secret type. Defaults to Opaque
renew is an optional secret renewal time in seconds
secretClaims: []
- name: secretName required
path: testPath required
type: kubernetes.io/tls optional
renew: 60 optional
Below is the implementation of Jenkins Configuration as Code. Add a key under configScripts for each configuration area,
where each corresponds to a plugin or section of the UI. Each key (prior to | character) is just a label, and can be any value.
Keys are only used to give the section a meaningful name. The only restriction is they may only contain RFC 1123 \ DNS label
characters: lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens. The keys become the name of a configuration yaml file on the controller in
/var/jenkins_home/casc_configs (by default) and will be processed by the Configuration as Code Plugin. The lines after each |
become the content of the configuration yaml file. The first line after this is a JCasC root element, eg jenkins, credentials,
etc. Best reference is https:///configuration-as-code/reference. The example below creates a welcome message:
JCasC:
defaultConfig: true
configScripts: {}
welcome-message: |
jenkins:
systemMessage: Welcome to our CI\CD server. This Jenkins is configured and managed as code.
Ignored if securityRealm is defined in controller.JCasC.configScripts and
ignored if controller.enableXmlConfig=true as controller.securityRealm takes precedence
securityRealm: |-
local:
allowsSignup: false
enableCaptcha: false
users:
- id: "${chart-admin-username}"
name: "Jenkins Admin"
password: "${chart-admin-password}"
Ignored if authorizationStrategy is defined in controller.JCasC.configScripts
authorizationStrategy: |-
loggedInUsersCanDoAnything:
allowAnonymousRead: false
Optionally specify additional init-containers
customInitContainers: []
- name: custom-init
image: "alpine:3.7"
imagePullPolicy: Always
command: [ "uname", "-a" ]
sidecars:
configAutoReload:
If enabled: true, Jenkins Configuration as Code will be reloaded on-the-fly without a reboot. If false or not-specified,
jcasc changes will cause a reboot and will only be applied at the subsequent start-up. Auto-reload uses the
http:///reload-configuration-as-code endpoint to reapply config when changes to the configScripts are detected.
enabled: true
image: kiwigrid/k8s-sidecar:0.1.275
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources: {}
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 50Mi
How many connection-related errors to retry on
reqRetryConnect: 10
env:
- name: REQ_TIMEOUT
value: "30"
SSH port value can be set to any unused TCP port. The default, 1044, is a non-standard SSH port that has been chosen at random.
Is only used to reload jcasc config from the sidecar container running in the Jenkins controller pod.
This TCP port will not be open in the pod (unless you specifically configure this), so Jenkins will not be
accessible via SSH from outside of the pod. Note if you use non-root pod privileges (runAsUser & fsGroup),
this must be > 1024:
sshTcpPort: 1044
folder in the pod that should hold the collected dashboards:
folder: "/var/jenkins_home/casc_configs"
If specified, the sidecar will search for JCasC config-maps inside this namespace.
Otherwise the namespace in which the sidecar is running will be used.
Its also possible to specify ALL to search in all namespaces:
searchNamespace:
Allows you to inject additional/other sidecars
other: []
The example below runs the client for https://smee.io as sidecar container next to Jenkins,
that allows to trigger build behind a secure firewall.
https://jenkins.io/blog/2019/01/07/webhook-firewalls/triggering-builds-with-webhooks-behind-a-secure-firewall
Note: To use it you should go to https://smee.io/new and update the url to the generete one.
- name: smee
image: docker.io/twalter/smee-client:1.0.2
args: ["--port", "{{ .Values.controller.servicePort }}", "--path", "/github-webhook/", "--url", "https://smee.io/new"]
resources:
limits:
cpu: 50m
memory: 128Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 32Mi
Name of the Kubernetes scheduler to use
schedulerName: ""
Node labels and tolerations for pod assignment
ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/nodeselector
ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/taints-and-tolerations-beta-feature
nodeSelector: {}
terminationGracePeriodSeconds:
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
Leverage a priorityClass to ensure your pods survive resource shortages
ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/pod-priority-preemption/
priorityClassName:
podAnnotations: {}
Add StatefulSet annotations
statefulSetAnnotations: {}
StatefulSet updateStrategy
ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/statefulset/update-strategies
updateStrategy: {}
ingress:
enabled: false
Override for the default paths that map requests to the backend
paths: []
- backend:
serviceName: ssl-redirect
servicePort: use-annotation
- backend:
serviceName: >-
{{ template "jenkins.fullname" . }}
Dont use string here, use only integer value!
servicePort: 8080
For Kubernetes v1.14+, use networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
For Kubernetes v1.19+, use networking.k8s.io/v1
apiVersion: "extensions/v1beta1"
labels: {}
annotations: {}
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
Set this path to jenkinsUriPrefix above or use annotations to rewrite path
path: "/jenkins"
configures the hostname e.g. jenkins.example.com
hostName:
tls:
- secretName: jenkins.cluster.local
hosts:
- jenkins.cluster.local
often you want to have your controller all locked down and private
but you still want to get webhooks from your SCM
A secondary ingress will let you expose different urls
with a differnt configuration
secondaryingress:
enabled: false
paths you want forwarded to the backend
ex /github-webhook
paths: []
For Kubernetes v1.14+, use networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
For Kubernetes v1.19+, use networking.k8s.io/v1
apiVersion: "extensions/v1beta1"
labels: {}
annotations: {}
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
configures the hostname e.g. jenkins-external.example.com
hostName:
tls:
- secretName: jenkins-external.example.com
hosts:
- jenkins-external.example.com
If youre running on GKE and need to configure a backendconfig
to finish ingress setup, use the following values.
Docs: https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/concepts/backendconfig
backendconfig:
enabled: false
apiVersion: "extensions/v1beta1"
name:
labels: {}
annotations: {}
spec: {}
Openshift route
route:
enabled: false
labels: {}
annotations: {}
path: "/jenkins"
controller.hostAliases allows for adding entries to Pod /etc/hosts:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/add-entries-to-pod-etc-hosts-with-host-aliases/
hostAliases: []
- ip: 192.168.50.50
hostnames:
- something.local
- ip: 10.0.50.50
hostnames:
- other.local
Expose Prometheus metrics
prometheus:
If enabled, add the prometheus plugin to the list of plugins to install
https://plugins.jenkins.io/prometheus
enabled: false
Additional labels to add to the ServiceMonitor object
serviceMonitorAdditionalLabels: {}
Set a custom namespace where to deploy ServiceMonitor resource
serviceMonitorNamespace: monitoring
scrapeInterval: 60s
This is the default endpoint used by the prometheus plugin
scrapeEndpoint: /prometheus
Additional labels to add to the PrometheusRule object
alertingRulesAdditionalLabels: {}
An array of prometheus alerting rules
See here: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/alerting_rules/
The `groups` root object is added by default, simply add the rule entries
alertingrules: []
Set a custom namespace where to deploy PrometheusRule resource
prometheusRuleNamespace: ""
Can be used to disable rendering controller test resources when using helm template
testEnabled: true
httpsKeyStore:
jenkinsHttpsJksSecretName:
enable: false
httpPort: 8081
path: "/var/jenkins_keystore"
fileName: "keystore.jks"
password: "password"
Convert keystore.jks files content to base64 ( cat keystore.jks | base64 ) and put the output here
jenkinsKeyStoreBase64Encoded: |
/u3+7QAAAAIAAAABAAAAAQANamVua2luc2NpLmNvbQAAAW2r/b1ZAAAFATCCBP0wDgYKKwYBBAEq
AhEBAQUABIIE6QbCqasvoHS0pSwYqSvdydMCB9t+VNfwhFIiiuAelJfO5sSe2SebJbtwHgLcRz1Z
gMtWgOSFdl3bWSzA7vrW2LED52h+jXLYSWvZzuDuh8hYO85m10ikF6QR+dTi4jra0whIFDvq3pxe
TnESxEsN+DvbZM3jA3qsjQJSeISNpDjO099dqQvHpnCn18lyk7J4TWJ8sOQQb1EM2zDAfAOSqA/x
QuPEFl74DlY+5DIk6EBvpmWhaMSvXzWZACGA0sYqa157dq7O0AqmuLG/EI5EkHETO4CrtBW+yLcy
2dUCXOMA+j+NjM1BjrQkYE5vtSfNO6lFZcISyKo5pTFlcA7ut0Fx2nZ8GhHTn32CpeWwNcZBn1gR
pZVt6DxVVkhTAkMLhR4rL2wGIi/1WRs23ZOLGKtyDNvDHnQyDiQEoJGy9nAthA8aNHa3cfdF10vB
Drb19vtpFHmpvKEEhpk2EBRF4fTi644Fuhu2Ied6118AlaPvEea+n6G4vBz+8RWuVCmZjLU+7h8l
Hy3/WdUPoIL5eW7Kz+hS+sRTFzfu9C48dMkQH3a6f3wSY+mufizNF9U298r98TnYy+PfDJK0bstG
Ph6yPWx8DGXKQBwrhWJWXI6JwZDeC5Ny+l8p1SypTmAjpIaSW3ge+KgcL6Wtt1R5hUV1ajVwVSUi
HF/FachKqPqyLJFZTGjNrxnmNYpt8P1d5JTvJfmfr55Su/P9n7kcyWp7zMcb2Q5nlXt4tWogOHLI
OzEWKCacbFfVHE+PpdrcvCVZMDzFogIq5EqGTOZe2poPpBVE+1y9mf5+TXBegy5HToLWvmfmJNTO
NCDuBjgLs2tdw2yMPm4YEr57PnMX5gGTC3f2ZihXCIJDCRCdQ9sVBOjIQbOCzxFXkVITo0BAZhCi
Yz61wt3Ud8e//zhXWCkCsSV+IZCxxPzhEFd+RFVjW0Nm9hsb2FgAhkXCjsGROgoleYgaZJWvQaAg
UyBzMmKDPKTllBHyE3Gy1ehBNGPgEBChf17/9M+j8pcm1OmlM434ctWQ4qW7RU56//yq1soFY0Te
fu2ei03a6m68fYuW6s7XEEK58QisJWRAvEbpwu/eyqfs7PsQ+zSgJHyk2rO95IxdMtEESb2GRuoi
Bs+AHNdYFTAi+GBWw9dvEgqQ0Mpv0//6bBE/Fb4d7b7f56uUNnnE7mFnjGmGQN+MvC62pfwfvJTT
EkT1iZ9kjM9FprTFWXT4UmO3XTvesGeE50sV9YPm71X4DCQwc4KE8vyuwj0s6oMNAUACW2ClU9QQ
y0tRpaF1tzs4N42Q5zl0TzWxbCCjAtC3u6xf+c8MCGrr7DzNhm42LOQiHTa4MwX4x96q7235oiAU
iQqSI/hyF5yLpWw4etyUvsx2/0/0wkuTU1FozbLoCWJEWcPS7QadMrRRISxHf0YobIeQyz34regl
t1qSQ3dCU9D6AHLgX6kqllx4X0fnFq7LtfN7fA2itW26v+kAT2QFZ3qZhINGfofCja/pITC1uNAZ
gsJaTMcQ600krj/ynoxnjT+n1gmeqThac6/Mi3YlVeRtaxI2InL82ZuD+w/dfY9OpPssQjy3xiQa
jPuaMWXRxz/sS9syOoGVH7XBwKrWpQcpchozWJt40QV5DslJkclcr8aC2AGlzuJMTdEgz1eqV0+H
bAXG9HRHN/0eJTn1/QAAAAEABVguNTA5AAADjzCCA4swggJzAhRGqVxH4HTLYPGO4rzHcCPeGDKn
xTANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADCBgTELMAkGA1UEBhMCY2ExEDAOBgNVBAgMB29udGFyaW8xEDAOBgNV
BAcMB3Rvcm9udG8xFDASBgNVBAoMC2plbmtpbnN0ZXN0MRkwFwYDVQQDDBBqZW5raW5zdGVzdC5p
bmZvMR0wGwYJKoZIhvcNAQkBFg50ZXN0QHRlc3QuaW5mbzAeFw0xOTEwMDgxNTI5NTVaFw0xOTEx
MDcxNTI5NTVaMIGBMQswCQYDVQQGEwJjYTEQMA4GA1UECAwHb250YXJpbzEQMA4GA1UEBwwHdG9y
b250bzEUMBIGA1UECgwLamVua2luc3Rlc3QxGTAXBgNVBAMMEGplbmtpbnN0ZXN0LmluZm8xHTAb
BgkqhkiG9w0BCQEWDnRlc3RAdGVzdC5pbmZvMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKC
AQEA02q352JTHGvROMBhSHvSv+vnoOTDKSTz2aLQn0tYrIRqRo+8bfmMjXuhkwZPSnCpvUGNAJ+w
Jrt/dqMoYUjCBkjylD/qHmnXN5EwS1cMg1Djh65gi5JJLFJ7eNcoSsr/0AJ+TweIal1jJSP3t3PF
9Uv21gm6xdm7HnNK66WpUUXLDTKaIs/jtagVY1bLOo9oEVeLN4nT2CYWztpMvdCyEDUzgEdDbmrP
F5nKUPK5hrFqo1Dc5rUI4ZshL3Lpv398aMxv6n2adQvuL++URMEbXXBhxOrT6rCtYzbcR5fkwS9i
d3Br45CoWOQro02JAepoU0MQKY5+xQ4Bq9Q7tB9BAwIDAQABMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAA4IBAQAe
4xc+mSvKkrKBHg9/zpkWgZUiOp4ENJCi8H4tea/PCM439v6y/kfjT/okOokFvX8N5aa1OSz2Vsrl
m8kjIc6hiA7bKzT6lb0EyjUShFFZ5jmGVP4S7/hviDvgB5yEQxOPpumkdRP513YnEGj/o9Pazi5h
/MwpRxxazoda9r45kqQpyG+XoM4pB+Fd3JzMc4FUGxfVPxJU4jLawnJJiZ3vqiSyaB0YyUL+Er1Q
6NnqtR4gEBF0ZVlQmkycFvD4EC2boP943dLqNUvop+4R3SM1QMM6P5u8iTXtHd/VN4MwMyy1wtog
hYAzODo1Jt59pcqqKJEas0C/lFJEB3frw4ImNx5fNlJYOpx+ijfQs9m39CevDq0=
agent:
enabled: true
defaultsProviderTemplate: ""
URL for connecting to the Jenkins contoller
jenkinsUrl:
connect to the specified host and port, instead of connecting directly to the Jenkins controller
jenkinsTunnel:
kubernetesConnectTimeout: 5
kubernetesReadTimeout: 15
maxRequestsPerHostStr: "32"
namespace:
image: "jenkins/inbound-agent"
tag: "4.6-1"
workingDir: "/home/jenkins"
customJenkinsLabels: []
name of the secret to be used for image pulling
imagePullSecretName:
componentName: "jenkins-agent"
websocket: false
privileged: false
runAsUser:
runAsGroup:
resources:
requests:
cpu: "512m"
memory: "512Mi"
limits:
cpu: "512m"
memory: "512Mi"
You may want to change this to true while testing a new image
alwaysPullImage: false
Controls how agent pods are retained after the Jenkins build completes
Possible values: Always, Never, OnFailure
podRetention: "Never"
You can define the volumes that you want to mount for this container
Allowed types are: ConfigMap, EmptyDir, HostPath, Nfs, PVC, Secret
Configure the attributes as they appear in the corresponding Java class for that type
https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-plugin/tree/master/src/main/java/org/csanchez/jenkins/plugins/kubernetes/volumes
volumes: []
- type: ConfigMap
configMapName: myconfigmap
mountPath: /var/myapp/myconfigmap
- type: EmptyDir
mountPath: /var/myapp/myemptydir
memory: false
- type: HostPath
hostPath: /var/lib/containers
mountPath: /var/myapp/myhostpath
- type: Nfs
mountPath: /var/myapp/mynfs
readOnly: false
serverAddress: "192.0.2.0"
serverPath: /var/lib/containers
- type: PVC
claimName: mypvc
mountPath: /var/myapp/mypvc
readOnly: false
- type: Secret
defaultMode: "600"
mountPath: /var/myapp/mysecret
secretName: mysecret
Pod-wide environment, these vars are visible to any container in the agent pod
You can define the workspaceVolume that you want to mount for this container
Allowed types are: DynamicPVC, EmptyDir, HostPath, Nfs, PVC
Configure the attributes as they appear in the corresponding Java class for that type
https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-plugin/tree/master/src/main/java/org/csanchez/jenkins/plugins/kubernetes/volumes/workspace
workspaceVolume: {}
- type: DynamicPVC
configMapName: myconfigmap
- type: EmptyDir
memory: false
- type: HostPath
hostPath: /var/lib/containers
- type: Nfs
readOnly: false
serverAddress: "192.0.2.0"
serverPath: /var/lib/containers
- type: PVC
claimName: mypvc
readOnly: false
Pod-wide environment, these vars are visible to any container in the agent pod
envVars: []
- name: PATH
value: /usr/local/bin
nodeSelector: {}
Key Value selectors. Ex:
jenkins-agent: v1
Executed command when side container gets started
command:
args: "${computer.jnlpmac} ${computer.name}"
Side container name
sideContainerName: "jnlp"
Doesnt allocate pseudo TTY by default
TTYEnabled: false
Max number of spawned agent
containerCap: 10
Pod name
podName: "default"
Allows the Pod to remain active for reuse until the configured number of
minutes has passed since the last step was executed on it.
idleMinutes: 0
Raw yaml template for the Pod. For example this allows usage of toleration for agent pods.
https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-pluginusing-yaml-to-define-pod-templates
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/
yamlTemplate: ""
yamlTemplate: |-
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
spec:
tolerations:
- key: "key"
operator: "Equal"
value: "value"
Defines how the raw yaml field gets merged with yaml definitions from inherited pod templates: merge or override
yamlMergeStrategy: "override"
Timeout in seconds for an agent to be online
connectTimeout: 100
Annotations to apply to the pod.
annotations: {}
Below is the implementation of custom pod templates for the default configured kubernetes cloud.
Add a key under podTemplates for each pod template. Each key (prior to | character) is just a label, and can be any value.
Keys are only used to give the pod template a meaningful name. The only restriction is they may only contain RFC 1123 \ DNS label
characters: lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens. Each pod template can contain multiple containers.
For this pod templates configuration to be loaded the following values must be set:
controller.JCasC.defaultConfig: true
Best reference is https:///configuration-as-code/referenceCloud-kubernetes. The example below creates a python pod template.
podTemplates: {}
python: |
- name: python
label: jenkins-python
serviceAccount: jenkins
containers:
- name: python
image: python:3
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
ttyEnabled: true
privileged: true
resourceRequestCpu: "400m"
resourceRequestMemory: "512Mi"
resourceLimitCpu: "1"
resourceLimitMemory: "1024Mi"
Here you can add additional agents
They inherit all values from `agent` so you only need to specify values which differ
additionalAgents: {}
maven:
podName: maven
customJenkinsLabels: maven
An example of overriding the jnlp container
sideContainerName: jnlp
image: jenkins/jnlp-agent-maven
tag: latest
python:
podName: python
customJenkinsLabels: python
sideContainerName: python
image: python
tag: "3"
command: "/bin/sh -c"
args: "cat"
TTYEnabled: true
persistence:
enabled: false
A manually managed Persistent Volume and Claim
Requires persistence.enabled: true
If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound
existingClaim:
jenkins data Persistent Volume Storage Class
If defined, storageClassName:
If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
storageClass:
annotations: {}
accessMode: "ReadWriteOnce"
size: "8Gi"
volumes:
- name: nothing
emptyDir: {}
mounts:
- mountPath: /var/nothing
name: nothing
readOnly: true
networkPolicy:
Enable creation of NetworkPolicy resources.
enabled: false
For Kubernetes v1.4, v1.5 and v1.6, use extensions/v1beta1
For Kubernetes v1.7, use networking.k8s.io/v1
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
You can allow agents to connect from both within the cluster (from within specific/all namespaces) AND/OR from a given external IP range
internalAgents:
allowed: true
podLabels: {}
namespaceLabels: {}
project: myproject
externalAgents: {}
ipCIDR: 172.17.0.0/16
except:
- 172.17.1.0/24
Install Default RBAC roles and bindings
rbac:
create: true
readSecrets: false
serviceAccount:
create: false
The name of the service account is autogenerated by default
name:
annotations: {}
imagePullSecretName:
serviceAccountAgent:
Specifies whether a ServiceAccount should be created
create: false
The name of the ServiceAccount to use.
If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template
name:
annotations: {}
imagePullSecretName:
Backup cronjob configuration
Ref: https://github.com/maorfr/kube-tasks
backup:
Backup must use RBAC
So by enabling backup you are enabling RBAC specific for backup
enabled: false
Used for label app.kubernetes.io/component
componentName: "backup"
Schedule to run jobs. Must be in cron time format
Ref: https://crontab.guru/
schedule: "0 2 * * *"
labels: {}
annotations: {}
Example for authorization to AWS S3 using kube2iam or IRSA
Can also be done using environment variables
iam.amazonaws.com/role: "jenkins"
"eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/jenkins-backup"
Set this to terminate the job that is running/failing continously and set the job status to "Failed"
activeDeadlineSeconds: ""
image:
repository: "maorfr/kube-tasks"
tag: "0.2.0"
Additional arguments for kube-tasks
Ref: https://github.com/maorfr/kube-taskssimple-backup
extraArgs: []
Add existingSecret for AWS credentials
existingSecret: {}
Example for using an existing secret
jenkinsaws:
Use this key for AWS access key ID
awsaccesskey: jenkins_aws_access_key
Use this key for AWS secret access key
awssecretkey: jenkins_aws_secret_key
Add additional environment variables
jenkinsgcp:
Use this key for GCP credentials
gcpcredentials: credentials.json
env: []
Example environment variable required for AWS credentials chain
- name: "AWS_REGION"
value: "us-east-1"
resources:
requests:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 1
limits:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 1
Destination to store the backup artifacts
Supported cloud storage services: AWS S3, Minio S3, Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage
Additional support can added. Visit this repository for details
Ref: https://github.com/maorfr/skbn
destination: "s3://jenkins-data/backup"
By enabling only the jenkins_home/jobs folder gets backed up, not the whole jenkins instance
onlyJobs: false
Enable backup pod security context (must be `true` if runAsUser or fsGroup are set)
usePodSecurityContext: true
When setting runAsUser to a different value than 0 also set fsGroup to the same value:
runAsUser: 1000
fsGroup: 1000
securityContextCapabilities: {}
drop:
- NET_RAW
checkDeprecation: true 执行以下命令开始安装jenkins
chart=jenkinsci/jenkinshelm install jenkins -n jenkins -f jenkins-values.yaml $chart执行安装
helm upgrade --install -f ../jenkins-values.yaml --setnameOverride=jenkins --namespace jenkins jenkins ../jenkins这会输出类似于以下内容的内容:
Release"jenkins"has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
NAME: jenkins
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu May2717:53:152021NAMESPACE: jenkins
STATUS: deployed
REVISION:1NOTES:
1. Get youradminuser password by running:
kubectlexec--namespace jenkins -it svc/jenkins -c jenkins -- /bin/cat /run/secrets/chart-admin-password&&echo2. Get the Jenkins URL to visit by running these commands in the same shell:echohttp://127.0.0.1:8080
kubectl --namespace jenkins port-forward svc/jenkins-master 8080:8080
3. Login with the password from step1and the username: admin查看
kubectl get pods -n jenkins
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
jenkins-master-0 2/2 Running03h38m我这里serviceType使用的是ClusterIPkubectl get svc -n jenkins
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S)AGE
jenkins ClusterIP 10.233.9.204 8080/TCP 3h40m
jenkins-agent ClusterIP 10.233.7.196 50000/TCP 3h40m
然后需要在本地映射端口访问
kubectl --namespace jenkins port-forward svc/jenkins 8080:8080
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 ->8080Forwarding from[::1]:8080 ->8080 访问:
localhost:8080
因为什么插件都没有安装,所以就是可以直接进去到jenkins界面
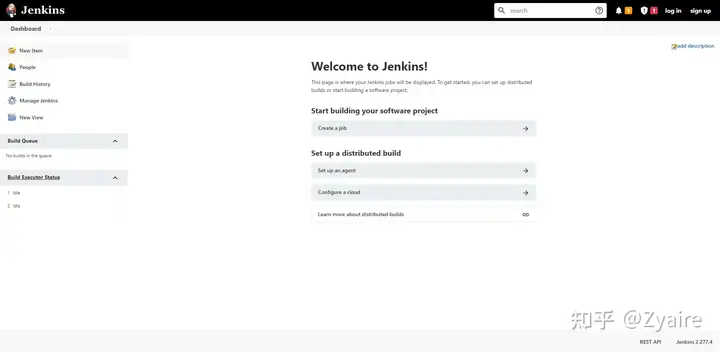
清除jenkins
helm uninstall jenkins -n jenkins如果觉得上面helm部署的方式比较麻烦大家可以尝试使用以下的方式部署。一样可以。
使用 YAML 文件的方式安装 Jenkins
- 准备部署文件jenkins-deployment.yaml
vim jenkins-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: jenkins
spec:
replicas:1selector:
matchLabels:
app: jenkins
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: jenkins
spec:
containers:
- name: jenkins
image: jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk11
ports:
- containerPort:8080volumeMounts:
- name: jenkins-home
mountPath: /var/jenkins_home
volumes:
- name: jenkins-home
emptyDir:{}创建部署
以下命令指示系统在 jenkins 命名空间内安装 Jenkins。
kubectl apply -f jenkins-deployment.yaml -n jenkins授予对 Jenkins 服务的访问权限
创建jenkins-service.yaml
$ vim jenkins-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: jenkins
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port:8080targetPort:8080selector:
app: jenkins创建服务
$ kubectl apply -f jenkins-service.yaml -n jenkins要验证创建服务是否成功,执行
$ kubectl get services -n jenkins
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S)AGE
jenkins NodePort 10.103.31.217 8080:33594/TCP 59s 访问 Jenkins 仪表板
从上面的输出中我们可以看到该服务已在端口 32664 上公开.
现在我们可以访问192.168.214.132:33594/的Jenkins实例
192.168.214.132是我的node节点ip
要访问 Jenkins,您最初需要输入您的凭据。新安装的默认用户名是 admin。可以通过多种方式获取密码。此示例使用 Jenkins 部署 pod 名称。
要查找 pod 的名称,请输入以下命令:
$ kubectl get pods -n jenkins找到 pod 的名称后,使用它来访问 pod 的日志。
$ kubectl logs -n jenkins 密码位于日志末尾,格式为长字母数字字符串:
*************************************************************
*************************************************************
*************************************************************
Jenkins initial setup is required.
An admin user has been created and a password generated.
Please use the following password to proceed to installation:
94b73ef6578c4b4692a157f768b2cfef
This may also be found at:
/var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword
*************************************************************
*************************************************************
*************************************************************使用以上密码登录jenkins并安装插件。
以上就是两种方式在k8s集群上部署jenkins。你学会了嘛?
如果想和我一起学习更多运维相关技术的话,欢迎大家在微信公众号中搜索【持续交付实践指南】,我会在上面不定期的发些工作实践中所用到的技术及问题。其实我也是才刚入行不到一年的小白,希望能够和大家共同进步~肝肝肝~



